Knowledge Base
How Rosetta Stone Works
Narrative's Rosetta Stone is instrumental in unlocking the full potential of data, acting as a universal interpreter for diverse datasets. It standardizes disparate data into a uniform, comprehensible structure, enabling seamless querying, joining, and consumption of data without the necessity for external mapping or cleaning.
Attributes
In the Narrative platform, attributes serve as the foundational elements of data, similar to fields in a database record. They detail every piece of data with specific information such as name, description, tags, validations, and type, thereby imparting structure and clarity.
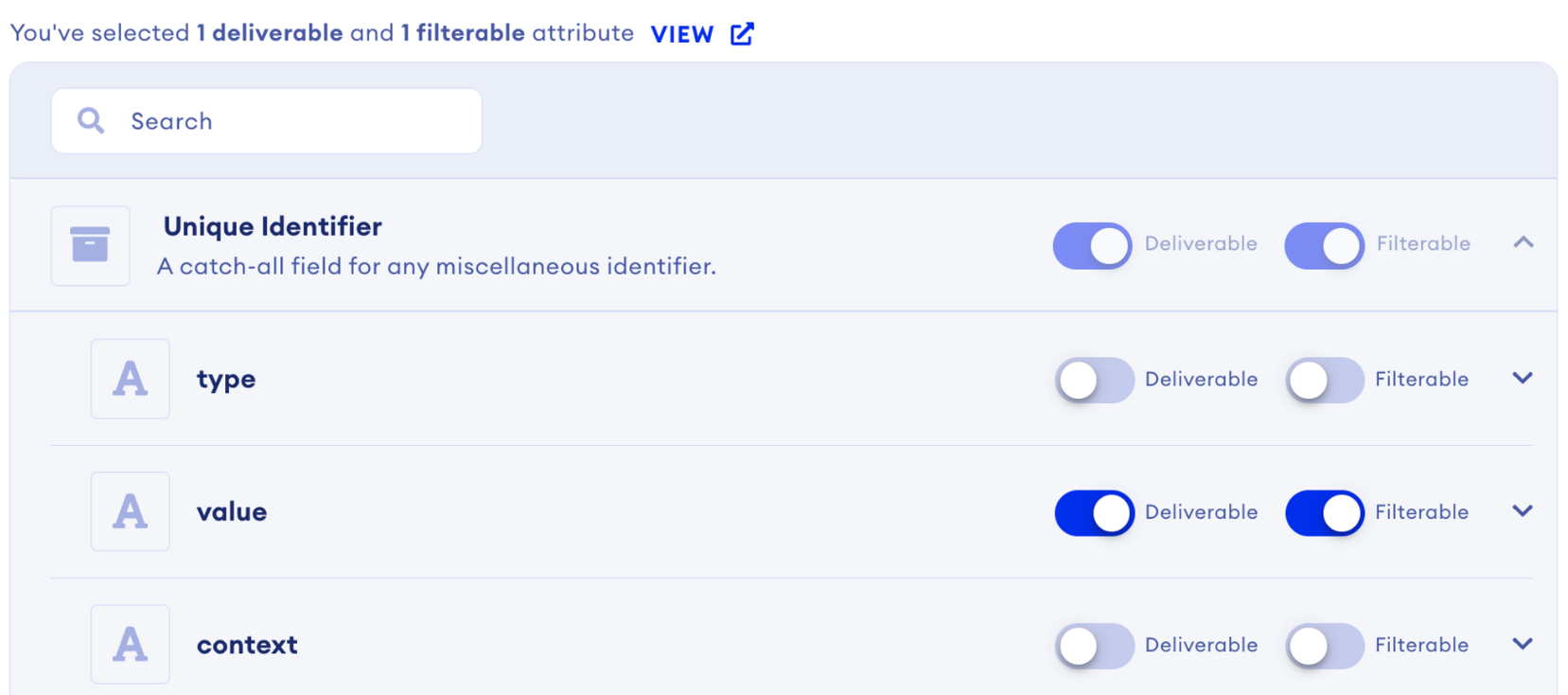
Example: Unique Identifier
A prime example is the Unique Identifier attribute, categorized as an “object” type. It comprises three fields: type, value, and context. This structure helps categorize and clarify data points aligned with the Unique Identifier, enhancing data organization and identification.
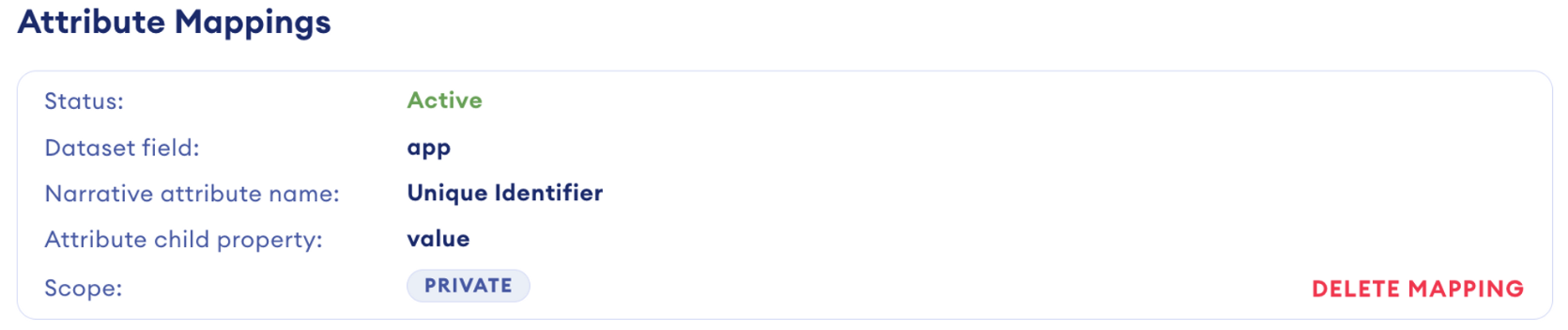
Mappings
Mappings are crucial for standardizing data across varied sources. By translating and normalizing data, mappings ensure its consistency and interpretability, simplifying the process of data interaction and utilization. Each mapping associates a specific attribute with a dataset column, facilitating straightforward data categorization. Moreover, mappings include a transformation process to represent each data point consistently according to the attribute's definition.
Rosetta Stone utilizes advanced machine learning techniques to automatically generate mappings, accurately identifying, labeling, and transforming dataset information into the appropriate format. While the system offers auto-generated mappings, users also have the option to suggest their mappings or create private ones, enhancing customization and precision.